Preserving heritage sites through innovative interpretation.
Through interpretation; education.
Through education; appreciation.
Through appreciation; protection.
- Freeman Tilden
A new generation of digital tools are proving valuable for heritage site managers. Interpretive innovation is allowing off-site visitors to explore and freely interact with a heritage site, allowing visitors to learn at ones own pace, and connecting through ones own interests. We have identified the interactive qualities that deliver a more immersive exploration, an experience that can build public appreciation and ultimately greater support.
How are sites digitally preserved?
Information Capture
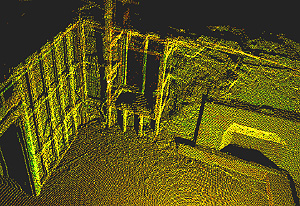
A detailed and multi-faceted snapshot of the site is captured. Measurable 3D spatial information is collected using survey-grade laser scanning, photogrammetry, GPS, and other remote sensing tools. Specialized forms of photography are used for detailed 2D visualization, and photography can be used for the purpose of creating 3D models. Historic data in the form of text, drawings, photography, maps, public records, and oral history is collected. Research uncovers the pieces required to tell the whole story.

Process & Analyze
Next, collected information is processed and analyzed. Digital analysis tools provide a new look at information that was once hidden or fragmented. A new synthesis of old information can reveal new insights. A Geographic Information System can be created to hold and analyze spatial information. Analysis of remote sensing data can allow us to see objects and locations we could not see before. Together these components form the basis for many deliverables that can serve conservation and dissemination purposes for heritage sites.
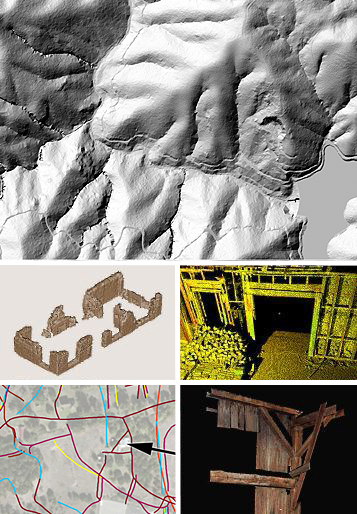
A rich dataset supports many deliverables.
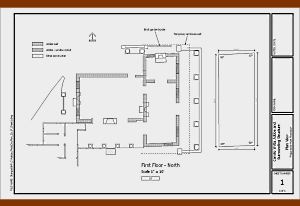
Measurable Drawings
Standardized Documentation

An Ultimate Archive